Google Shopping has transformed the retail industry. In the UK retail sector, 82% of ad spend is spent on Shopping ads, attracting 88% of paid search clicks.
Shopping ads also have a 28% higher conversion value per click than standard search ads. So they’re a good way to boost eCommerce revenue. Google Shopping ads are typically displayed above all other results in the search engine results page, which contributes to their high click rate:
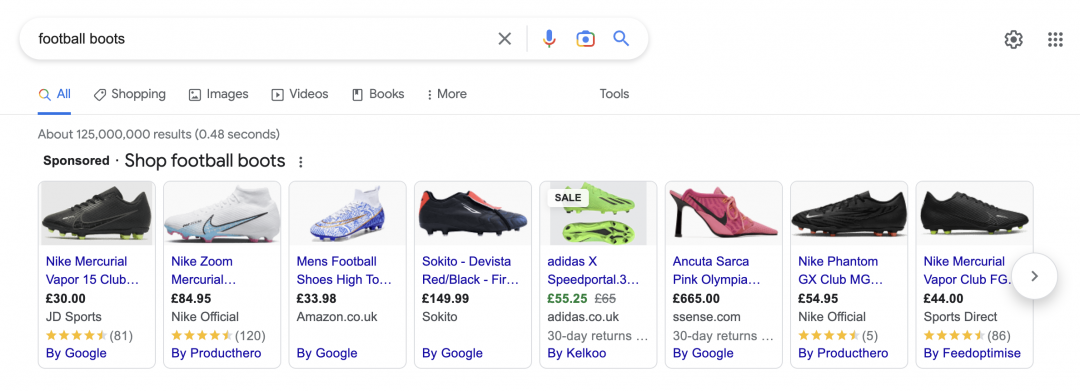
Sam Baldwin, founder of KeyCommerce, explains why Google Shopping ads are so effective:
"The way that Shopping ads are designed, a customer clicking on it has a pretty good idea of what the product is, and exactly how much it costs, which means there’s a higher chance they’re going to buy it. This is why we see that the conversion rates for Google Shopping campaigns are generally higher than the conversion rates for search campaigns."
Sam Baldwin
Founder of KeyCommerce
To get the best possible results, these Google Shopping feed best practices will help you set your campaigns for maximum ad spend efficiency.
TL;DR: Google Shopping feed best practices
Here’s a quick overview of the top ten ways to optimise your Google Shopping campaigns:
- Optimise your product titles — Make sure product titles include your highest converting keywords, as well as essential buyer information.
- Write creative product descriptions — Apply SEO principles to your product description, and be honest, creative, and compelling.
- A/B test your product titles and descriptions — Experiment with variations on product details to ensure they’re fully optimised.
- Optimise your landing pages — Check product details are consistent and correct across your ads and landing pages.
- Get creative with product types — Create custom product types to signal who your ads and products are for.
- Make use of all supported attributes — Add attributes like colour, size, gender, and material to your product feed.
- Decide if you need a GTIN — Find out whether a Global Trade Item Number will help or hinder your Google Shopping campaigns.
- Upgrade your product images — Take photos that exceed the minimum requirements and show your product in its best light.
- Protect your Shopping ads from bots — Prevent invalid traffic from depleting your ad budget with automated PPC efficiency software like Lunio.
- Make use of custom labels — Improve campaign management by categorising your products with custom labels.
In a recent episode of the Paid Media Lab podcast, we spoke to PPC expert Selina Patel about all things Standard Shopping vs. PMax. It's definitely worth watching if you're after key Standard Shopping tips & tricks from one of the best in the business:
Watch more episodes of the Paid Media Lab for in-depth paid media discussions with industry experts.
Otherwise, here's how to optimize your Google Shopping feed:
1. Optimise your product titles
Product titles are the most important element of your Google Shopping feed. According to John Moran, co-founder and senior client strategist at Solutions 8:
"50 to 60% of your feed optimisation is going to be off of that product title. Now, there’s obviously going to be other areas that have an effect on the inbound search traffic, but that title is one of the most important."
John Moran
Founder of Solutions 8
The product title tells Google what your product actually is. It acts like an SEO search term: if you want someone searching for “football boots” to see your ad, you need to make sure that keyword is in the product title.
A good way to optimise your product titles is to check out the search terms and search categories your shopping ad is already showing for. You can view these in the Insights tab:
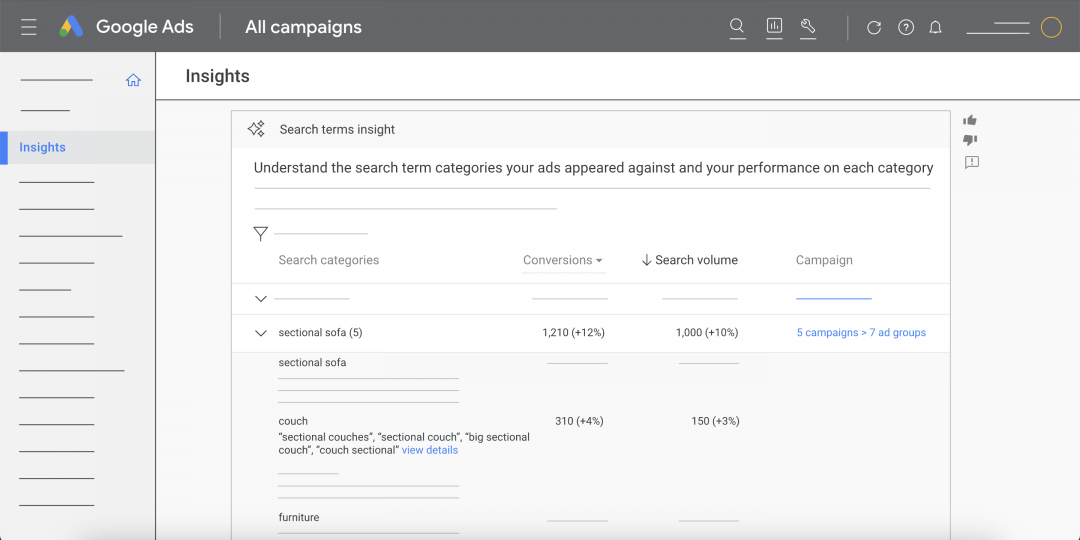
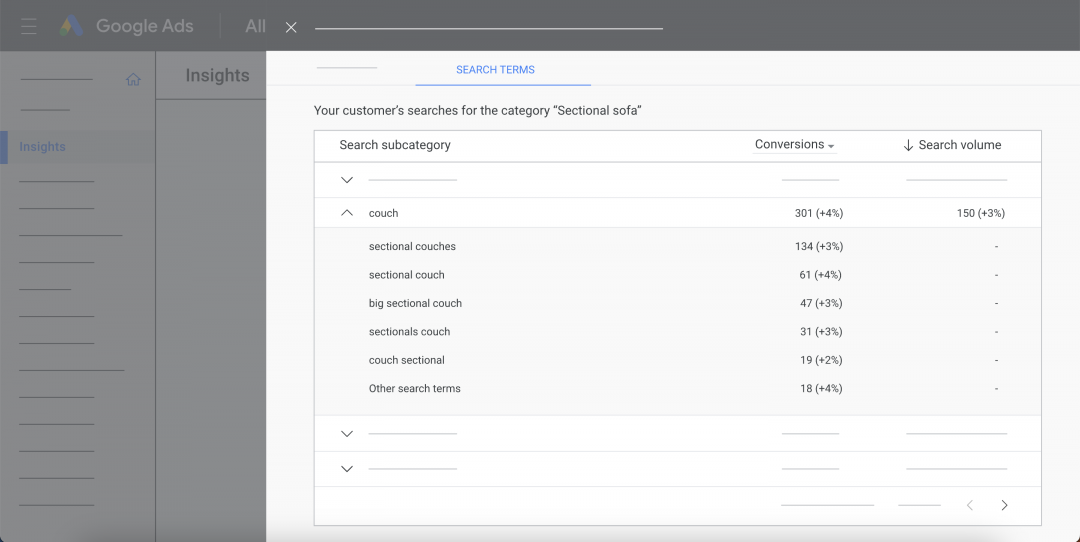
The insights report gives you lots of useful information grouped by search category or search term, including:
- Clicks
- Impressions
- Click-through rate (CTR)
- Conversions
- Conversion rate
- Conversion value
- Search volume (across targeted countries)
With this data, you can make conscious, data-driven decisions to optimise your product title. Make sure search terms and search category terms with the highest conversion rates feature in your product title.
Google allows you to use up to 150 characters in a Shopping product title, but it only displays up to 70. So while we recommend making use of the full character limit, put the information you want potential buyers to see within the first 70 characters. The rest can be used to include secondary keywords and other information.
The product title isn’t just about keywords. Use this spot to highlight benefits that differentiate you from competing products, such as:
- Product design — Is it handmade, vintage, or designer?
- Ease of use — Is it a simple product, or does it require expertise?
- Cost — Is it on sale, or a luxury item?
Adding this extra info can also improve conversion rates. It means your ad is less likely to be served to people looking for products you don’t sell. If you only sell kids’ football boots, avoid appearing for searches for adults’ football boots by highlighting this in the title.
2. Write creative product descriptions
In your product description, you can talk about your product in a more creative, less keyword-driven way (although these are still important).
If you’re familiar with SEO, apply the same principles when writing your product description. Be honest, descriptive, and compelling. Here’s an example:
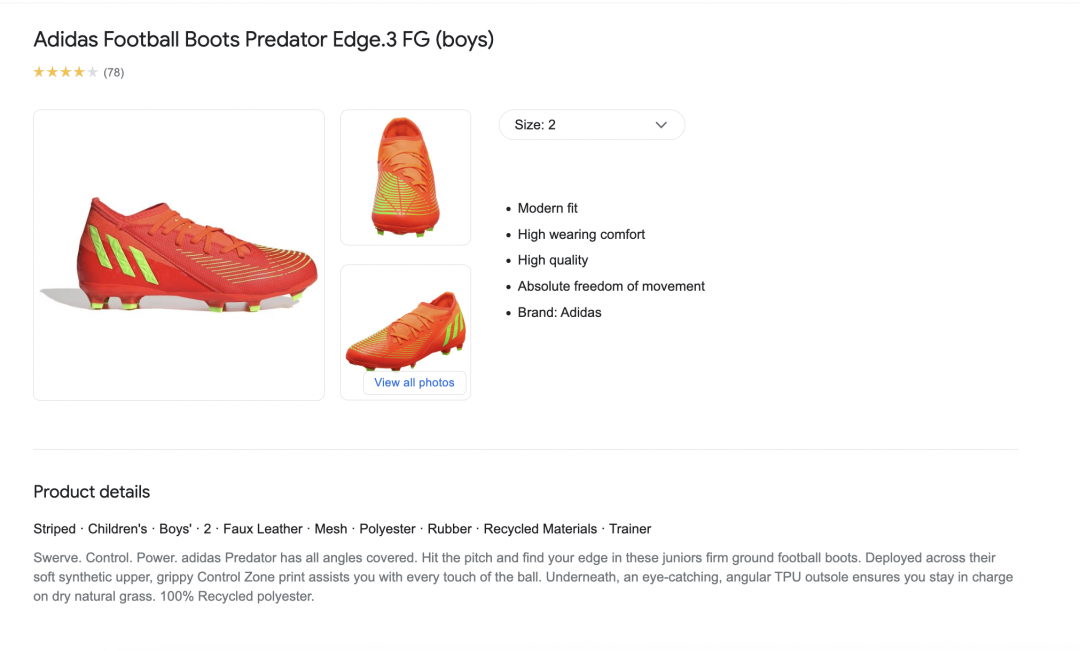
This description ticks all the boxes:
- Keyword-optimised — “find your edge in these juniors firm ground football boots”
- Creative — “Swerve. Control. Power.”
- Honest — “stay in charge on dry natural grass”
- Descriptive — “across their soft synthetic upper, grippy Control Zone print assists you”
- Compelling — “hit the pitch and find your edge”
If your product description is well-optimised, Google can use it to seek out similarities with other products and find more super-relevant traffic for you. So after your product title, this is the second most important area of feed optimisation.
3. A/B test your product titles and descriptions
A/B testing helps you find the ad variant that will generate most conversions. But unfortunately, Google’s built-in experimentation feature doesn’t support Shopping campaigns. Unlike search campaigns, you can’t run multiple ads for the same product at the same time.
There are two approaches you can take:
- Run one version of your ad for a specific period (at least a month, but longer if you can). Then make one change to your ad, run it for the same period, and compare results.
- Create separate products based on attributes, such as colour, price, or quantity. You can then test different titles and descriptions for each product variant.
When you’ve established which title and description works best, make sure your feed title matches your website’s product title, so customers know exactly what they’re getting.
4. Optimise your landing pages
Like any PPC campaign, there should be consistency and continuity between ads and landing pages in your Google Shopping campaigns.
When you’ve optimised your product data feed, make sure to update your landing pages with the same information. Here’s what a well-optimised Shopping ad and landing page looks like:
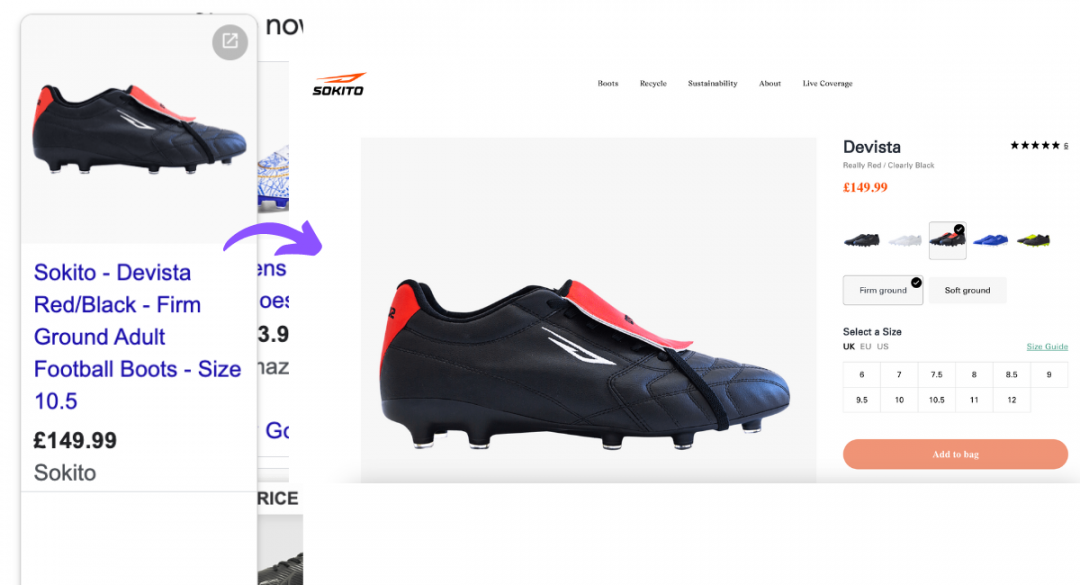
With the exception of size, all attributes are pre-selected on click-through, including colour and ground type. The price and brand name also match, giving the customer clarity and confidence in your product and making them more likely to buy.
5. Get creative with your product type
Let’s head back to your optimised Google Shopping feed and take a look at your product type, which can be found within product attributes.
While Google has its own product taxonomy (which is predefined in the Google product category) you can use the product type field to create your own product categorisation system. Here are some example product types:
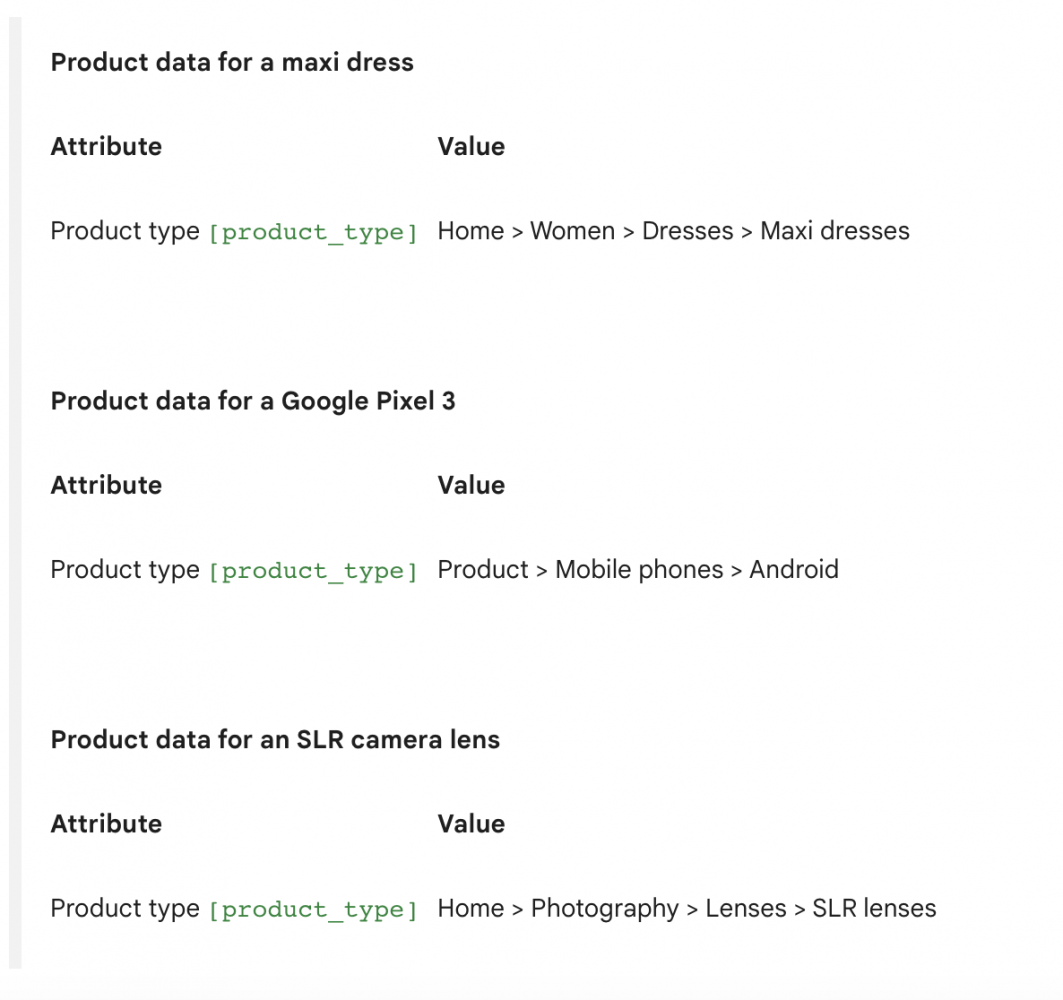
Creating your own subcategories tells Google who should view your ads, especially if your product doesn’t fit well into one of the predefined categories. For example, football boots don’t have their own category in Google’s product taxonomy; the closest is “Sporting Goods > Athletics > Soccer > Soccer Protective Gear.”
A product type value such as “Football > Football Kit > Football Boots” might be more indicative of who these products (and ads) are relevant for.
6. Make use of all supported attributes
Google Shopping supports several different attributes. Some are mandatory, some are optional, and some depend on other factors. Everything we’ve covered so far is required (with the exception of product type, which is optional but highly recommended).
In addition to these, there are lots of other optional product identifiers you can include. We recommend using as many as apply to your product, as this improves ad relevance and makes it easier for Google to find matching traffic.
This table shows which product identifier attributes Google supports and when they’re needed:
| Required | Sometimes Required* | Optional |
| Image link | Additional image link | Cost of goods sold |
| Stock availability | Mobile link | Expiry date |
| Price | Stock availability date | Sale price |
| Adult product indicator | Brand | Sale price effective date |
| Global Trade Item Number | Unit pricing measure | |
| Condition | Subscription cost | |
| Multipack | Energy efficiency class | |
| Bundle | Product dimensions | |
| Age group | Product weight | |
| Colour | Product detail | |
| Gender | ||
| Material | ||
| Pattern | ||
| Size |
*See when specific identifier attributes are required.
Try to maintain consistency in your attributes, especially when it comes to sizing and colour. The colours in your feed should match those on your site (for example, don’t describe your boots as pink in your feed if the colour is listed as coral on your website).
Set up feed rules in your Google Merchant Center account to add product attributes quickly and easily. Find out how to set up feed rules in this video:
7. Decide if you need a GTIN
A Global Trade Item Number (or GTIN) may be required in your Google Shopping campaign. Google lists the GTIN as “required (for all products with a known GTIN to enable full offer performance)” but also “optional (strongly recommended) for all other products.”
So what is a GTIN, and do you actually need one?
A GTIN is a number that identifies a product no matter where it’s sold. Unlike an SKU, which is often unique to a particular store, a GTIN is the same everywhere. It’s often found on barcodes:
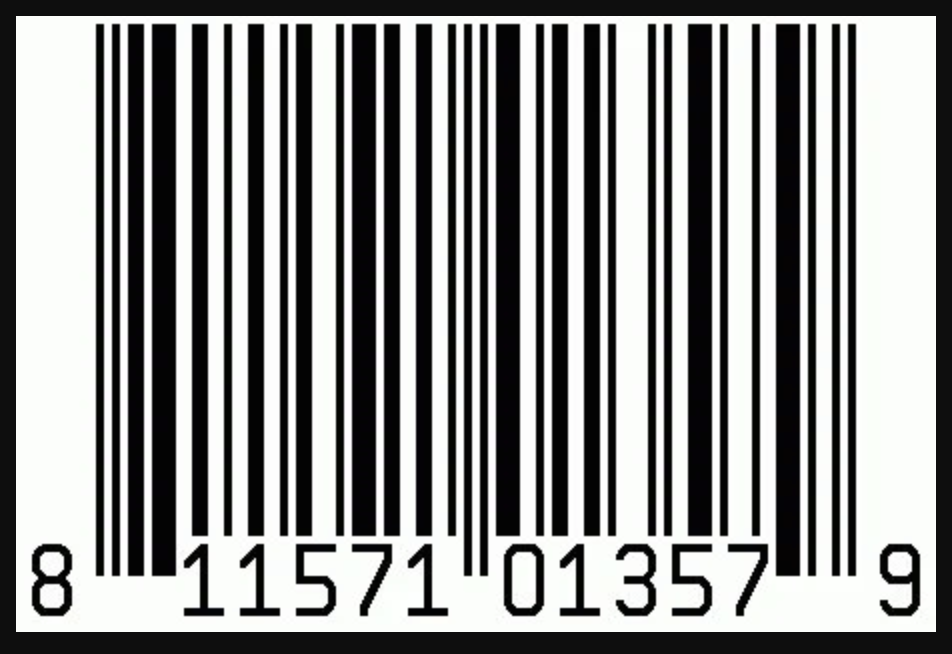

Including a GTIN in your product feed gives you a share of any traffic searching for that specific product. But according to John, this can be both useful and dangerous:
"When you’re talking about GTIN, the way it can help you is if you’re reselling a product that already has a GTIN. It’s going to give you that immediate traffic. If you’re the manufacturer, it can hurt you. The traffic you’ve generated yourself is also being targeted by your competitors and distributors selling your product."
John Moran
Founder of Solutions 8
When you’re an established brand, this might not matter. Nike football boots are sold all over the world in thousands of stores, so there’s more to this competition than whether or not advertisers have included a GTIN in their product feed.
But if you’re a young business with a unique product, sharing your traffic with distributors might not be the most profitable approach.
8. Upgrade your product images
Great images are essential for a successful Google Shopping campaign. Photos that show your product in its best light (and display features specific to relevant search queries) are likely to attract more clicks.
Google requires photos that are 100 x 100 pixels as a minimum. But this is pretty tiny; larger, higher-res images tend to perform better. It’s recommended that your images are at least 800 x 800 pixels.
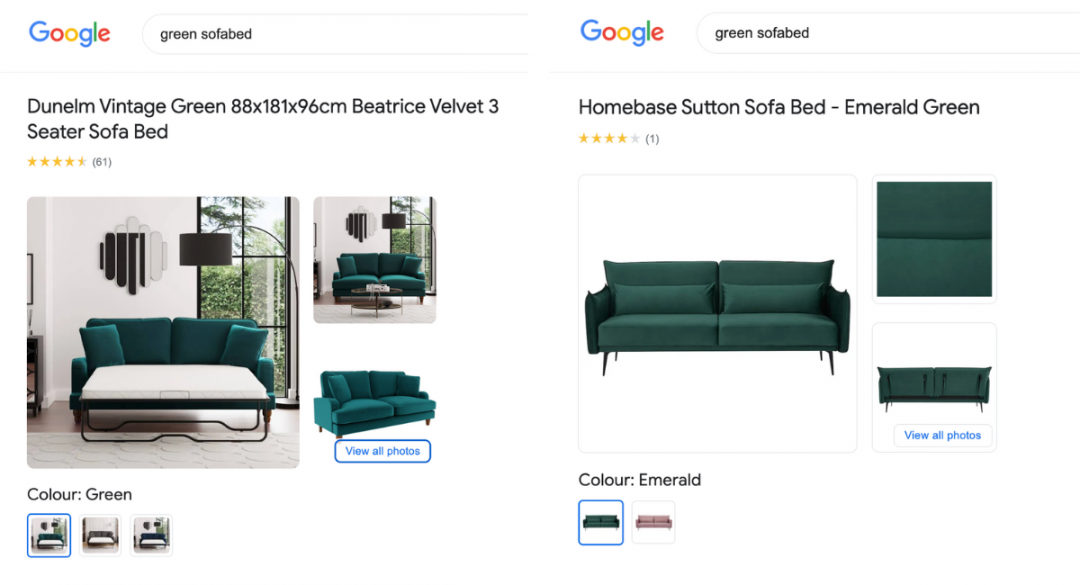
The first ad includes photos of the sofabed in situ, giving shoppers a better idea of how it can fit into their home. It also shows the item as both a sofa and a sofabed, so shoppers know what to expect.
The second ad has high-quality images, but they don’t offer much more insight than the main photo. More clicks are then needed to find out more about the product, increasing conversion barriers.
9. Protect your Shopping ads from bots
All PPC campaigns are vulnerable to fake clicks from bots and fake users, including your Google Shopping ads. So protecting your campaigns against invalid traffic is another top way to boost sales and minimise wasted spend.
There are a few ways to do eliminate invalid traffic from your campaigns:
- Monitor click-through and conversion rates — High CTR with a very low conversion rate can indicate bot activity.
- Set up IP exclusion lists — These must be monitored manually and continually updated when new bots are identified.
- Monitor Google Analytics — Landing page metrics like bounce rate and time spent on page can signal that fake users are clicking on your ads.
- Use automated software — Automatically identify bots and fake users before the click, and prevent them from interacting with your ads.
Lunio makes your Shopping campaigns more efficient by automatically preventing fake users from clicking your ads. You can reduce wasted ad spend by up to 25% and use that money to drive additional conversion volume. It’s one of the fastest ways to improve ROI from your performance marketing. You can get a 14-day free trial to see Lunio in action for yourself.
10. Make use of custom labels
Custom labels won’t necessarily improve your Shopping campaign performance, but they can make it a lot easier to manage. This boosts your PPC efficiency, so it’s worth taking the time to set them up.
Custom labels allow you to subdivide the products in your Shopping or Performance Max campaign using your own values. For example, you can add labels for:
- Bestsellers
- Clearance items
- Seasonal products
- Price bands
- Profit margin bands
Categorising your products with custom labels then allows you to adjust your bids based on these groups, depending on your goals.
Get more from Google Shopping
Ultimately, the more accurate, relevant information you can feed into your Google Ads account, the more you can optimise your Google Shopping campaigns.
By taking the time to adjust your product titles and descriptions, set up custom labels and product types, and eliminate invalid traffic from your campaigns, you’ll kickstart your sales without increasing your spend.



